Science
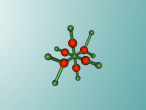
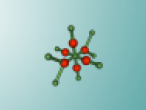
Calcium Chloride
Introduction
This blog will detail the composition, structure and characteristics of calcium chloride and includes
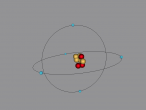
Boron Atom (By Melody Suen)
At the QUT workshop, I learnt how to use VRMath 2.0 to program, create 3D molecules/atoms and how to write a blog. With my partner Hana, we created a 3D model of a boron atom. In this blog post, I will explain the composition, structure and characteristics of boron, as well as the programming used.
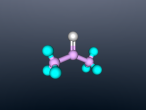
Acetone Blog
My name is Michaela Cheong and I am a student at Brisbane State High School. In our current unit of science, we are learning about chemistry, specifically the structure and characteristics of atoms (building blocks which make up everything) and compounds (consist of two or more atoms which are chemically bonded). In this blog, I will show you a 3D model of a molecule of acetone along with a discussion of it’s molecular structure, uses and properties.
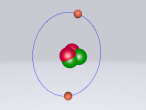
Nitrogen Atom
It is an element that is an essential to all life on Earth, yet in its purest form it can suffocate living organisms. Nitrogen is one of the most important elements on Earth – it can be found in all living systems and makes up around 78% of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is a constituent of protein and nucleic acids. In its gaseous form, nitrogen is colourless, odourless and generally considered inert. In its liquid form nitrogen is also colourless and odourless, and resembles water. Nitrogen was first recognised in 1772 by number of scientists; Carl Wilhelm Scheele, Daniel Rutherford, Henry Cavendish and Joseph Priestley, who all found that air was composed of three different gases, oxygen, carbon dioxide and another gas which they dubbed ‘foul air’ (nitrogen). Nitrogen was first recognised as an element by Antoine Laurent Lavoiser in 1786, and named nitrogen in 1790 by Antoine Laurent Lavoiser. Today, nitrogen is used in food preservation, explosives, and aids medical research.