Engineering
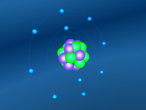
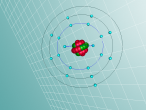
Neon Atom
The atom being researched is Neon. It is the 10th element in the Periodic Table. It was discovered in 1898 by William Ramsay and Morris Travers at Universiity College London. The name comes from the Greeek 'Neos,' meaning 'new'. It is a rare gaseous element that, when in a vacuum discharge tube, emits a reddish-orange glow.
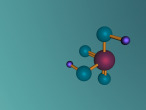
Sulphuric Acid
Sulphuric Acid
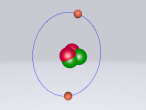
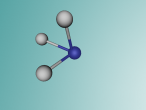
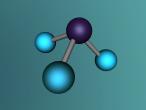
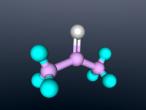
Ammonia Molecule
Ammonia (NH3) is a molecule which consists of three hydrogen atoms and a nitrogen atom bonded together. It is a colourless, odorous, alkaline gas which is produced when organic materials decompose. This molecule is essential to many plants and animals, as a source of nitrogen. Additionally, bacteria within the intestines can produce the substance. Ammonia has many uses, though it is mostly used in fertilisers and cleaning products.
The Potassium Atom
Potassium is a chemical element classified the atomic symbol 'K' on the Periodic Table. As the seventh most abundant element on Earth (2.6% abundance in Earth's crust), potassium is found in a wide array of industries, despite being commonly known for its integral role as a mineral that allows human cell function and its presence in bananas. Some applications of potassium are (but not limited to) potassium-based fertilisers, pharmaceuticals and manufacturing. Discovered in 1807 by Sir Humphrey Davy, its abundance and simple atomic structure has allowed for exhaustive research and application regarding potassium.
A Neon Atom (Blog)
Chemistry and the idea of matter was first suggested by John Dalton in 1805 in his 'Atomic Theory' and over the century has been expanded on by many other scientists. Chemistry is the scientific category about substances of matter and their properties, compositions and the different reactions that take place when mixed together. Matter has a defined mass, takes up space and is composed of a mixture of elements. An element contains a group of only one type of atom. To identify elements refer to the periodic table which shows all elements with similar atomic structure and there atomic numbers. Atoms are the smallest parts that matter and elements can be divided into and are commonly known as the 'building blocks' of life.