Science
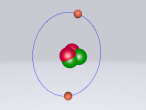
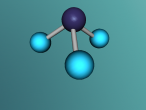
Ammonia molecule
Atoms are the basic building blocks of all matter. This means that everything around you, including yourself, are made up of atoms. However, what happens when these atoms join together chemically? Well, they form compounds called molecules. Molecules are composed of chemically-bonded atoms and they have a neutral charge unlike an ion, meaning that they have the same amount of protons and neutrons total. Atoms can never be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction, so they can only break off and form new molecules. Ammonia is a type of molecule and is composed of of one nitrogen atom and three hydrogen molecules, with the chemical equation being NH3. It is described as a colourless, pungent gas. The major use of ammonia is in fertilisers because they are a great source of nitrogen in fertilisers (nitrogen enhances leaf growth). The chief commercial method of producing ammonia is by the Haber-Bosch process, involving the direct reaction of elemental hydrogen and elemental nitrogen. Its boiling point is -33.35oC and its freezing point is -77.7oC.
Aluminium Blog
My partner and I decided to investigate the atom ‘Aluminium’ and proceeded to research about. Through our research, we found that aluminium is a chemical element in the boron group with the symbol Al and atomic number of 13. It is a silvery-white, light-weight metal that is soft and malleable (Royal Society of Chemistry). Aluminium is the third most plentiful element in the earth’s crust, comprising 8% of the planet’s soil and rocks (Lenntech). In nature, aluminium is found only in chemical compounds with other elements such as sulphur, silicon and oxygen, however pure metallic aluminium can be economically produced from aluminium oxide ore or extracted from bauxite by electrolysis (Australian Government – Geoscience Australia). There are several uses of this metal including packaging materials such as foil and cans as well as the construction of transport i.e. automobiles, aircraft fuselages etc. (HowItsMade).

FINAL Methane Blog by Anna Lei (ASC092A)
The compound methane has the chemical formula of CH4. Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon of the paraffin series and a potent greenhouse gas, as well as being a large component of natural gas. The major human-associated source of methane is the production/combustion of coal (Britannica, 2016). In nature, methane is the product of anaerobic bacterial decomposition and certain human/animal activities (7% methane in flatulence). It can be found in wetlands, termites, landfills, volcanoes and oceans. The abundance of methane makes it a widely used fuel for heat and light (energy) production (ARM, 2016). In this blog, the details of methane will be uncovered.
- 2 comments
- Read more
- 4253 reads
Neon Atom
The atom being researched is Neon. It is the 10th element in the Periodic Table. It was discovered in 1898 by William Ramsay and Morris Travers at Universiity College London. The name comes from the Greeek 'Neos,' meaning 'new'. It is a rare gaseous element that, when in a vacuum discharge tube, emits a reddish-orange glow.
Silicon Atom
My partner and I have decided to research and create a 3D model of the element silicon. Silicon is an element present in the periodic table, possessing the atomic number of 14. Its atomic mass number is 28.085 and its state at room temperature is solid. It is known to be the "seventh most abundant element in the universe and the second most abundant element in the Earth's crust" (Gagnon, S., n.d.). Silicon has various uses including improving the strength of aluminium alloys, helping the operation of electronic products in the form of chips and being the main material that solar panels are made of (SIMCOA, n.d.). Most silicon on earth is found in the crust as sand, quartz and rock crystals among others. The discovery of silicon is credited to Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius in 1824. He heated chips of potassium in a silica container then washed away the byproducts.